6 Min Read | 17 Feburuary 2023 | Key Words: IPv4 Address, IPv6 Address
“IPv6 is the first and might be the last upgrade of the global network in the coming decades. ” said in a report by the Beijing Internet Institute.
Google statistics reveal many countries have rates of 0%, while a few, such as India and Germany, have rates of over 50%. (Graph1: source from Google)

Graph1:Per-Country IPv6 adoption
Gaph1 shows that there is still a long way to go before IPv6 is fully popularized. There has been no significant progress in IPv6 deployment in several regions of the world.
Google is continuously measuring the availability of IPv6 connectivity among Google users. The graph shows the percentage of users that access Google over IPv6. (Graph2: source from Google)
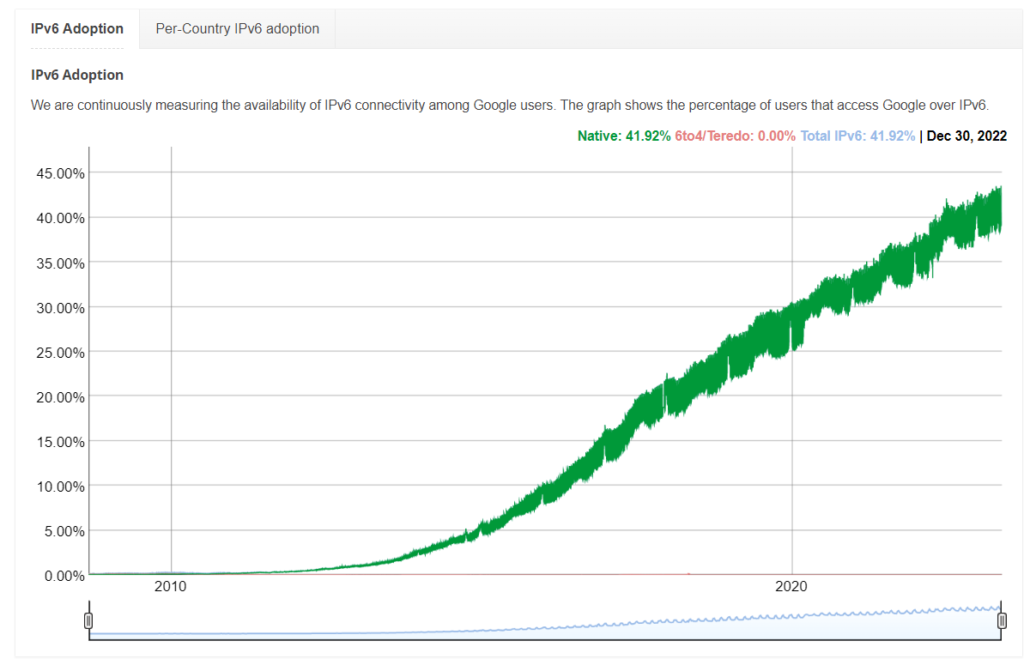
The change in the percentage of Google users accessing IPv6 over the past decade shows the increasing ratio of IPv6.
Reasons why IPv6 is used nowadays instead of IPv4?
Limitations of IPv4
IPv4 addresses are drying up due to the rapid growth of Internet users, high usage of devices such as phones, laptops and computers, inefficient use of addresses, and always-on devices such as cable modems.
The need for IPv6
Being developed to overcome IPv4’s address exhaustion, IPv6 is introduced to replace IPv4 and is often referred to as the “next generation Internet” due to its enhanced features and growth in recent years.
What is IP Address?
An IP address is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a network of computers that communicate using Internet protocol. IP addresses are required for devices on a network to communicate with each other.
There are two main types of IP addresses : IPv4 and IPv6.
Know more about IPv6 Address
1. What is IPv6?
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), and is an upgrade of IPv4. IP version 6 allows data communications to pass packets over a network involving sending and receiving data in the form of packets between 2 nodes in a network.
IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, and is intended to replace IPv4.
IPv6 addresses are written in hexadecimal format, like this:
2a02:afc0:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000
2. How does IPv6 work?
IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, theoretically allowing a total of 340 trillion trillion addresses. Unlike the IPv4 address method, which uses 4r sets of 1 to 3 digit numbers, IPv6 uses eight groups of 4 hexadecimal digits separated by colons.
IP version 6 handles data packets more efficiently, improving performance and security. It helps Internet service providers reduce the size of routing tables by making them more hierarchical.
3. Types and scope of IPv6
The three types of IPv6 addresses are: global unicast addresses, unique local addresses, and link-local addresses.
- Global unicast addresses, which are, routable over the Internet and start with 2001. The prefix of an international unicast address comes from the information passed by the router in the network notification.
- Unique local addresses, which should be used on an internal network, such as LAN. They are routable on the internal network, but not on the internet.
- Link-local addresses, which will be used as an internal network. They are routable on the internal network, but not on the internet. It is essential that each IPv6 interface must be configured with a link-local address even if there is no route.
Know more about IPv4 Address
1. What is IPv4?
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It is one of the foundational protocols of standards-based internetworking methods on the web.
A typical IPv4 address has 32 bits and is in dotted-decimal format, like this:
185.233.16.8
Distinction between IPv6 and IPv4
Benefits of using IPv6
1. Larger address space
IPv6 uses four times more bits to address devices over the Internet.
2. Simplified header
IPv6 headers have a new simplified header format designed to be simpler and easier to handle than IPv4.
3. End-to-end connectivity
With IPV6, each machine now has a unique IP address and can traverse the Internet without the need for NAT or other translation elements.
4. Auto-configuration
Automatic configuration not only ensures the uniqueness of links, but also determines the information that should be automatically configured.
5. Faster forwarding or routing
IPv6 features a streamlined header that puts all the extra information last. The information in the front part of the header is enough to make a routing decision quickly, making the routing decision process as fast as looking at the mandatory header part.
6. No broadcast
IPv6 uses multicast addresses to communicate with multiple hosts because IPv6 does not support any broadcast addresses. For one-to-many communication, multicast addresses are used.
7. Stronger security through IPSec
IPSec is used at the network processing layer to ensure network security.
It seems IPv6 is the furture, However……
Global IPv6 adoption has a long way to go
The protocol’s designers believed that IPv6 would become widespread around 2003 as IPv4 addresses dwindled.
However, till 2019 when the last IPv4 was officially exhausted, IPv6 still hadn’t been adopted on a large scale.

Regardless of the deployment of IPv6, the Internet will continue to run on IPv4. While we await a wider adoption of IPv6, we need to find ways to manage IPv4, since it is exhausting.
IP leasing provides a solution that helps us extend the availability of IPv4 as we continue to migrate to IPv6.
To address the IPv4 shortage and figure out how to build a sustainable Internet with the resources available, IPv4 Superhub Limited offers IPv6 as well as IPv4 rental and purchase services. We maximize the value of idle IP resources worldwide.